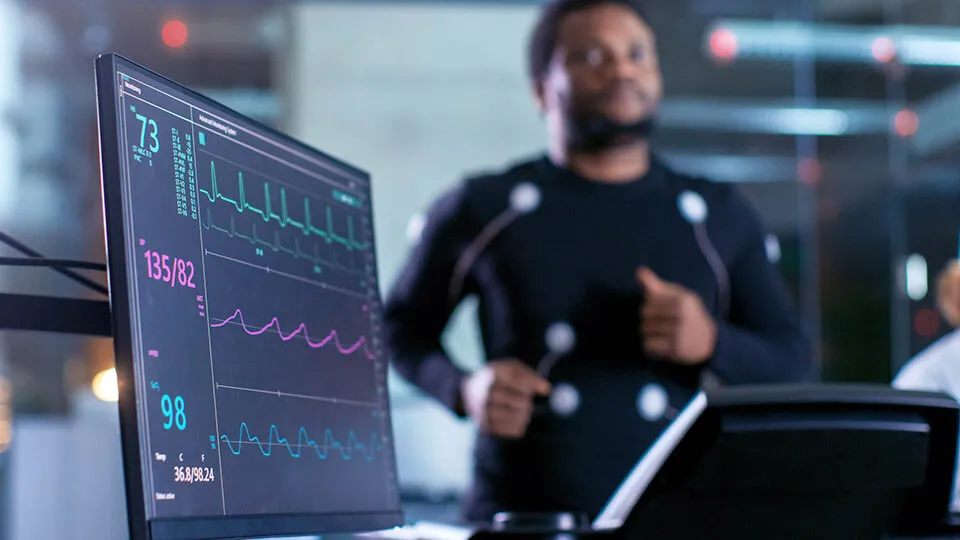
The heart is one of the body's most vital organs, as it pumps the blood that fuels human function. Heart disease and other heart conditions are some of the most common issues facing Americans, and health care providers must understand how to diagnose and monitor these concerns. Let's examine some of the most common cardiovascular tests you can perform and explore what situations require them.
Common Cardiovascular Tests
The following 10 cardiovascular tests provide medical professionals with information about how a patient's heart functions.
Electrocardiogram
Do You Know the Four Major Vital Signs?
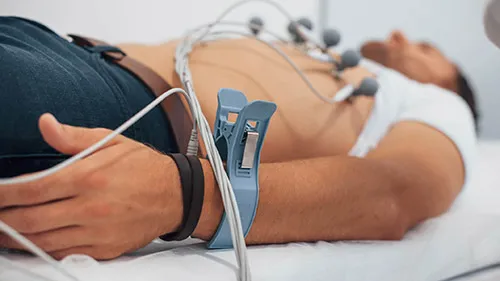
You can use an electrocardiogram (an ECG or EKG) to determine how regular a patient's heartbeat is and gain a clear understanding of any rhythmic issues an individual may be experiencing. To perform an electrocardiogram, an EKG technician attaches sensors that record the electric movement the heart sends to a patient's body. An electrocardiogram machine captures the data, which a technician can analyze to determine any concerns.
Electrocardiograms help medical professionals understand how often a patient's heart is beating, how regular these beats are, and how quickly the heart works. An EKG can be beneficial for concerns about a patient's heart construction. For example, an EKG may detect signs of an artery blockage in the heart. These tests are crucial when diagnosing a heart attack, treating a heart condition before a heart attack occurs, or diagnosing an arrhythmia.
Related: Echocardiographers: Cardiac Imaging Experts
Exercise Stress Test
The heart needs to perform effectively during aerobic exercise. An exercise stress test (1) allows a technician to monitor how a patient's heart responds to cardiovascular activity. The test results can be vital in determining the individual's overall heart health and helping the person prepare for intense physical exercise. During an exercise stress test, a technician connects the patient to an EKG machine while the individual walks or jogs on a treadmill. Some technicians perform this test on a stationary bike instead of a treadmill.
While the patient exercises, a technician monitors heartbeat, blood pressure, and breathing. The EKG results can help determine whether the patient has proper blood flow to the heart. This test can help diagnose heart disease or arrhythmia.
Echocardiogram Ultrasound
An echocardiogram (2) is an ultrasound of the heart that visually represents the patient's heart and its activity through sound waves. A sonographer must place a gelled transducer on the patient's chest to perform an ultrasound. The ultrasound produces images of the heart's sound waves on the monitor.
An echocardiogram can help identify any issues with heart valves or chambers. When patients note they're experiencing chest pain or having trouble breathing deeply, an echocardiogram may help eliminate a heart condition as the potential cause. A health care professional can also perform an echocardiogram for an expecting parent to diagnose prenatal congenital disabilities, such as congenital heart failure.
Interested In How To Become a Cardiac Sonographer?
Click here to explore Cardiovascular Sonography Programs near you!
Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE)
A TEE (3) is an echocardiogram performed by inserting a probe into a patient's esophagus to take pictures of the heart and its functions using sound waves. This type of echocardiogram requires sedation for the patient. The sonographer inserts the transducer down the throat, through which the technician can access the esophagus. A TEE helps take detailed images of the heart's upper chambers and valves.
A health care professional might order a TEE if the provider is concerned about valve disease or other valve issues. This test can also help identify blood clots in the heart, which can be highly dangerous if left untreated. TEEs are more invasive than standard echocardiograms but provide more detailed images of the heart and its environment. A TEE can also be beneficial if the patient is obese, as it gives more precise shots of the heart.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
An MRI test (4) uses radio waves and a magnetic field to provide a comprehensive image of a patient's heart. A technician applies dye to the heart to make certain areas easier to interpret, and an MRI could capture still images or videos of the heart to help technicians understand how it functions. An MRI can be a beneficial tool for examining the condition of a patient's heart after trauma.
For example, an MRI could reveal any damage if a patient suffers a stroke, and a doctor wants to learn if it affected the heart, blood vessels surrounding the heart, or valves. MRIs can also diagnose issues with heart muscle, iron deposits, aorta inflammation, heart disease, and other cardiac conditions.
Blood Test

What You Need to Know About Blood Types
A simple blood test (5) is one of the most common approaches to evaluating a patient's general heart health. Blood tests can identify risk factors like high cholesterol. They could also denote heart damage after trauma, like a heart attack, as these events sometimes release substances into a patient's blood that indicate a cause for concern. Standard blood panels typically evaluate levels of sodium, potassium, peptides, triglycerides, lipids, troponin, and full blood count (FBC).
High or low levels of these substances in the blood could denote heart issues like heart disease, heart failure, hypertension, heart damage, and more. A blood panel is often the first step in diagnosing severe heart issues. To perform a blood test, a phlebotomist typically extracts the necessary amount of blood, which lab technicians then test.
Nuclear Cardiac Stress Test
The nuclear cardiac stress test (6) adapts the exercise stress test with imaging. This imaging test helps health care providers capture an image of the blood flow to and from a patient's heart. During a nuclear cardiac stress test, also called a myocardial perfusion scan or a dual isotope treadmill test, a technician injects a small amount of a radioactive substance, called a radionuclide, into the patient's bloodstream. This substance increases blood flow in the body.
Then, a small camera takes images of how the blood moves to and from the heart. You can use this test to ensure a patient's heart can receive ample blood the rest of the body sends to it. If a technician notices obstructed blood flow or areas of the heart without radionuclide, it could indicate the patient has a blockage in an artery.
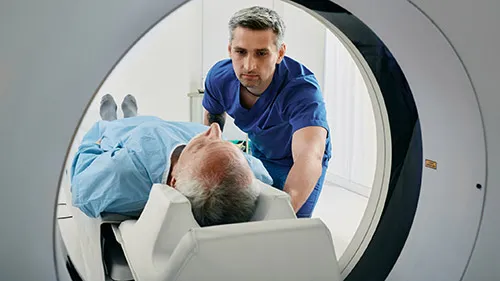
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan
Just What Equipment Do Diagnostic Medical Sonographers Use?
A CT scan (7) is an X-ray that takes pictures of a patient's heart from various angles. During this test, a technician attaches electrodes to a patient's body before the individual enters the CT scanner. The scan generates 3D images of the patient's heart. This cardiovascular test can be beneficial after a patient has suffered a stroke, as it allows you to examine the heart and blood vessels for damage.
CT scans could also be a tool for identifying artery blockage. To ensure the scanner generates precise, clear images, the patient must stay as still as possible during the process. A health care professional may supplement a coronary CT scan with scans of the arteries or aorta for a more comprehensive view of the patient's heart health.
Tilt-Table Test
If a patient is experiencing lightheadedness or fainting spells, a tilt-table test (8) can help investigate the issue and analyze the heart's response to a change in gravity. During this test, the patient sits on an angled table. A technician monitors blood pressure and pulse to learn whether the tilted posture affects blood flow or heartbeat.
The tilt-table test could help diagnose arrhythmia and other heart rhythm issues. Many causes exist for dizziness, lightheadedness, and faintness. Tilt-table tests can rule out heart-related causes like bradycardia, an abnormally slow heart rate. Faintness and dizziness can also be a side effect of new medications or a sign of blood pressure issues. It's essential to learn whether the heart faces stress while these symptoms occur so that a health care provider can develop a proactive care plan.
Ambulatory Rhythm Monitoring Tests
Sometimes, the tests performed in a health care setting, such as at a hospital, clinic, or doctor's office, provide only some of the data needed to make an informed decision about a patient's care. A health care provider can supply the patient with a wearable device in these cases. These ambulatory rhythm monitoring (9) devices record patients' heart activity during everyday life, such as while eating, walking, sleeping, and working.
Devices for ambulatory rhythm monitoring include Holter and mobile cardiac telemetry monitors. These devices can also be helpful for patients who don't feel heartbeat abnormalities but show symptoms of a heart condition. Monitoring can provide a record of any indistinguishable rhythm issues in the patient. When analyzing the results of an ambulatory rhythm monitoring test, it's essential to look for abnormalities. Some symptoms, such as an irregular heartbeat, might not be consistently present, but they may appear frequently enough for concern. Review test results carefully.
If you're interested in helping individuals with heart conditions find treatment and pursue a better life, Concorde Career Colleges can help. We have health care education programs in nursing, diagnostics, patient care, and more. Schedule a tour at a location near you today to learn more about how you can get the education you need to launch a rewarding career in health care.
Footnotes
1. Stress Test, Mayo Clinic, https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/stress-test/about/pac-20385234#:~:text=A%20stress%20test%20usually%20involves,creates%20the%20effects%20of%20exercise
2. Echocardiogram, Mayo Clinic, https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/echocardiogram/about/pac-20393856#:~:text=A%20technician%20(sonographer)%20spreads%20gel,moving%20images%20on%20a%20monitor
3. Echocardiogram Types, Stanford Healthcare, https://stanfordhealthcare.org/medical-tests/e/echocardiogram/types.html
4. Heart MRI, Cleveland Clinic, https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/21961-heart-mri
5. Tests for Diagnosing Heart Conditions, National Health Service (NHS) Scotland Inform, https://www.nhsinform.scot/illnesses-and-conditions/heart-and-blood-vessels/common-tests/tests-for-diagnosing-heart-conditions
6. Guide to Nuclear Stress Test, Weill Cornell Medicine, https://cardiology.weillcornell.org/sites/default/files/downloads/guide_to_nuclear_stress_test_1_0.pdf
7. Heart CT Scan, Medline Plus, https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007344.htm
8. Tilt-Table Test, American Heart Association, https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/heart-attack/diagnosing-a-heart-attack/tilt-table-test
9. Ambulatory Monitors, Cleveland Clinic, https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/16732-ambulatory-monitors#:~:text=Ambulatory%20monitors%20are%20devices%20that,outside%20of%20a%20medical%20setting.
Take The Next Step Towards a Brighter Future
Interested in learning more about our Cardiovascular Sonography program?
We have a Concorde representative ready to talk about what matters most to you. Get answers about start dates, curriculum, financial aid, scholarships and more!