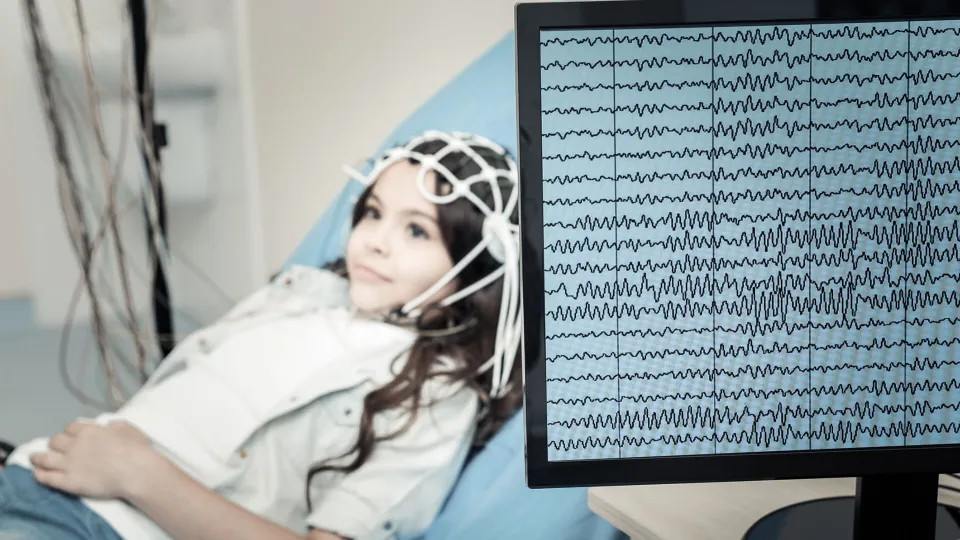
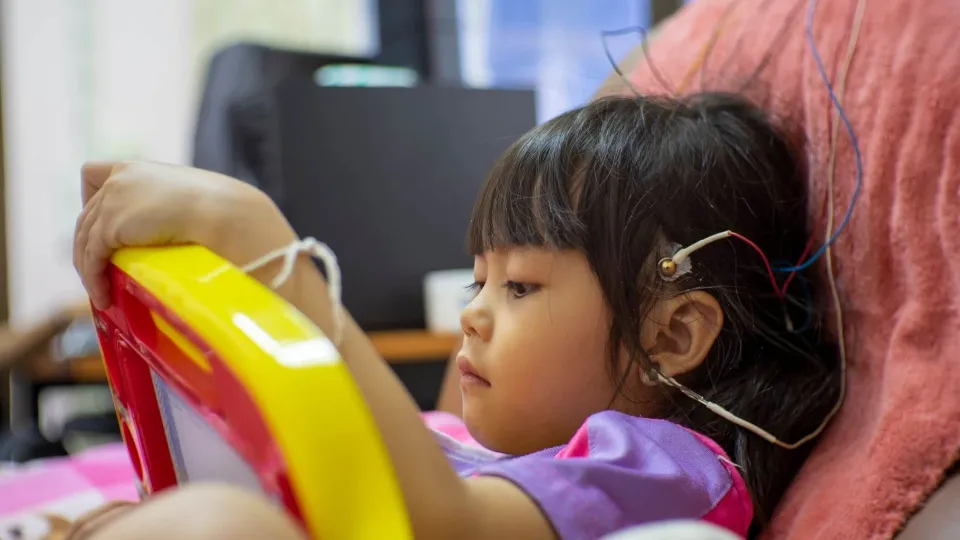
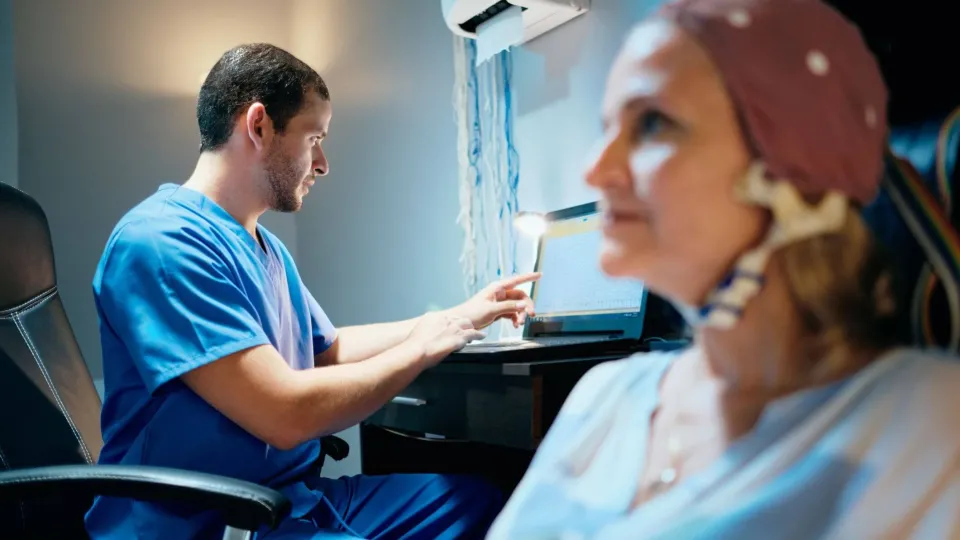
A neurodiagnostic technologist (NDT) specializes in recording electrical activity in the brain and nervous system for diagnostic purposes. They use specialized equipment to determine how effectively a patient's nervous system is functioning.
The test results that are gathered enable physicians to diagnose and treat conditions such as degenerative brain diseases, headaches, dizziness, seizure disorders, strokes, mental disorders, and sleep disorders. By recording electrical patterns throughout these systems, neurodiagnostic technologists provide valuable data that physicians use to make diagnoses and treat conditions.
5 Types of EEG tests for brain wave monitoring
The most common tests performed by a neurodiagnostic technologist are electroencephalograms (EEG) to assess the quality and/or presence of brain activity. There are numerous tests an EEG tech can run so let's take a look at a few of the more common ones given.
Standard EEG test

A doctor may order a standard EEG test if a patient is experiencing symptoms such as persistent headaches, unexplained seizures or behavioral changes.
Results from these tests are used to check for any abnormal brain waves that may be an indication of more serious underlying health conditions. Further tests may be required for making a diagnosis if an abnormality is found or detected.
A Standard EEG test is usually done on an outpatient basis at a hospital or clinic. The whole process may take up to two hours with the actual recording taking as little as 20 minutes. After which the patient is free to go back home.
If the patient is being reevaluated, then the doctor may ask them to stop taking currently prescribed medications a day before the test. This is done so that whatever abnormal symptoms that the patient was being treated for can be reevaluated during the test.
Sleep EEG test
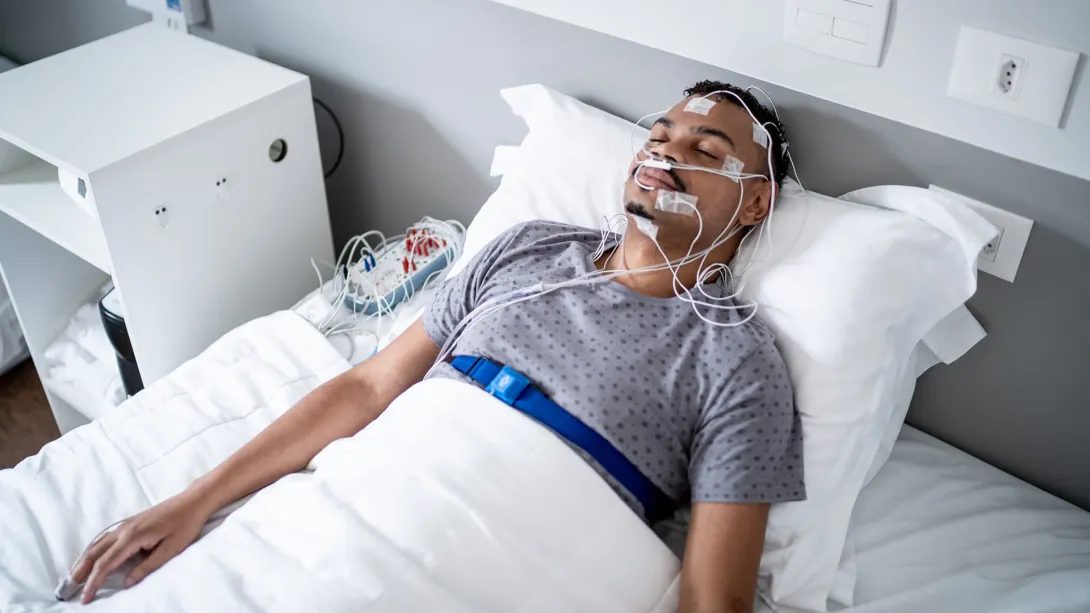
When a person is sleeping, the brain wave activity is different from the awake state and some types of abnormal waves are more easily detected when the patient is sleeping.
Sometimes seizures happen when the patient is asleep. Sleep EEG tests are done very much like standard EEG tests with the only exception being the patient will be asleep during the test.
Patients having difficulty relaxing and falling asleep may be given medications to assist in falling asleep. In such cases, patients may need assistance in returning home or need to stay back a few extra hours at the hospital.
Sleep-deprived EEG test
A Sleep-deprived EEG test is similar to the Sleep EEG tests but the patient is asked to deprive themselves of sleep. It is a test done to improve the possibility of detection of abnormal brain wave activities. The possibility of detecting abnormal brain waves is also much higher when the patient does not have enough sleep or is tired.
In preparation for this test, the patient may be asked to stay awake the previous night or get up earlier than usual. The test is usually conducted in the morning and all caffeine should be completely avoided before a test is given.
Interested In How To Become a Neurodiagnostic Technologist?
Click here to explore Neurodiagnostic Technology Programs near you!
Ambulatory EEG test
When a patient is experiencing unexplained seizure episodes at random intervals these episodes become very difficult to predict and if all previous tests failed to capture a seizure episode, an Ambulatory EEG test is prescribed.
Ambulatory EEG is a test similar to the standard EEG test in the type of information it records, with the added benefit that the patient can be mobile and is not confined to the testing center. Ambulatory means being able to walk.
This EEG test device uses similar electrodes like a standard EEG test; however, they are all connected to a self-contained compact recording device that can be carried around like a previous generation portable radio.
The patient is free to go through their daily routine while the device continuously records all brain wave activities. The test period can range from few hours to few days.
The patient is asked to keep a record of all their activities during the test period. The patient will also need an assistant who can watch them during the test period in case a seizure occurs. The assistant will be able to record helpful details about the incident.
After the testing phase is completed, the doctor can compare the written records with actual brain wave data (electroencephalogram) and get a clearer understanding of what was happening during a seizure episode.
Neurofeedback EEG test
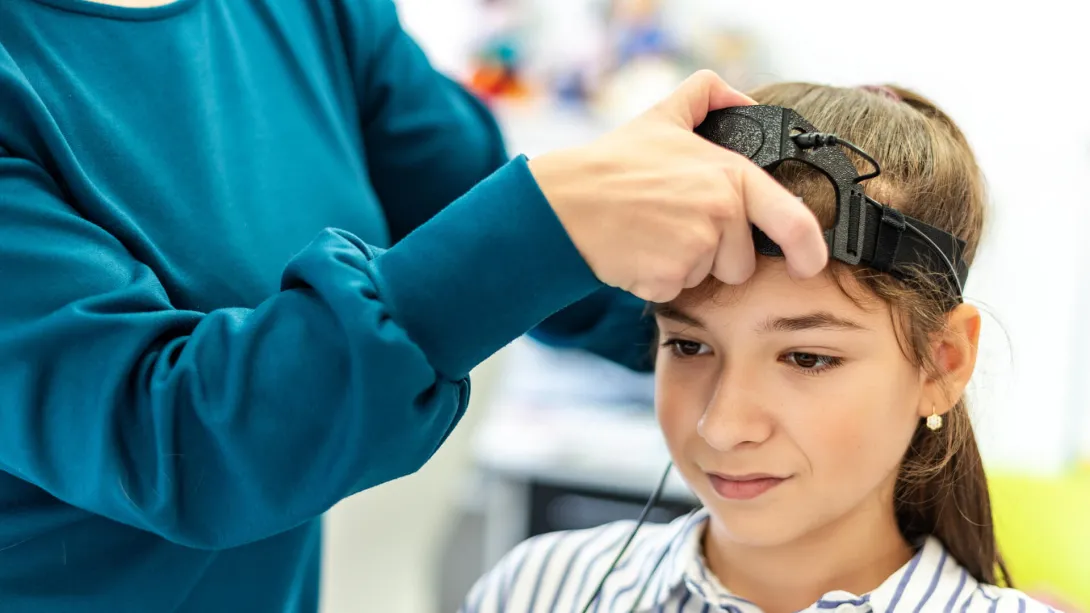

Neurofeedback, also known as EEG biofeedback, is a kind of brain training activity done with the help of an EEG machine. This procedure is designed to alter and improve the brainwave activity, thereby helping the patient overcome undesirable conditions like depression, anxiety, eating disorders etc.
Children suffering from Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) can also benefit greatly from this procedure.
In many cases, the test procedure can be used for making life-changing improvements in patients suffering from various mental illnesses. The patient will need to take multiple sessions for this procedure to be most effective. This procedure is noninvasive and is deemed perfectly safe for patients.
There is lots of research done that shows the effectiveness of this procedure. Most of the skills learned during procedure remain for a lifetime and can improve a patient's learning ability, mood, attention span, memory, and more.
Did you know...
Concorde Career College has a Neurodiagnostic Technology program that can be completed in as few as 18 months? If you'd like to learn more about this exciting program or any of our other healthcare career training programs, contact us today!
Take The Next Step Towards a Brighter Future
Interested in learning more about our Neurodiagnostic Technology program?
We have a Concorde representative ready to talk about what matters most to you. Get answers about start dates, curriculum, financial aid, scholarships and more!